Chapter's Questionnaire

1. What are the three general principles of DEVELOPMENT? And what implications does this have for us teachers?
- People
develop at different rates
- Development
is relatively orderly
- Development
takes place gradually
We as teachers must pay close attention to those students who are less mature in their thinking and social relationship to help them improve these skills, also we should study them in terms of their learning process, behavior, if someone has learning disabilities, to focus on how we can help them without ignoring the children who do not suffer such disorders.
2. What is the gray matter of the brain?
Neurons because they are grayish color, and sometimes they are called gray matter of the brain.
3. What is synaptic plasticity?
Communication between neurons by synaptic transmissions can be strength or weak depending of patterns of use, so the strength of these synaptic connections is always changing.
4. How different is the experience-expectant process from the experience-dependent?
Experience-expectant develop in large areas of the brain which explains why people have pronunciation problems that is not part from their native language, and in the other hand experience-dependent is based on individual´s experiences and they are formed to neutral activities in localized areas of the brain.
5. Do children need expensive toys to be stimulated? Explain.
No, because we can teach in public or private schools in the first one, they do not have enough money to buy expensive toys to stimulate a kid instead they can use chipper things and they will be the same arouse than a child from a private school.
6. Describe the cerebral cortex.
The cerebral cortex allows the greatest human accomplishments, such as problem solving and language. It is the last part of the brain to develop, so it is more susceptible to environmental influences than other areas of the brain. First matures the region of the cortex that controls physical motor movement, then the senses such as vision, and hearing, and at least the frontal lobe that controls higher- order thinking process. The temporal lobes of the cortex that play major roles in emotions, judgment, and language develop until high school years or later.
7. What is meant by lateralization?
Half of the brain controls the opposite side of the body, damage to the right side of the brain will affect movement of the left side of the body and vice versa. Certain areas of the brain affect behaviors. The left hemisphere of the brain is a major factor in language processing, and the right hemisphere handles much of our spatial visual information and emotions. For some left-handed people, the relationship may be reversed, but for most left handers and for females on average, there is less hemispheric specialization altogether.
8. What does "High horse power, poor steering" mean when defining adolescence? How can teachers take advantage of their intensity?
It means that individual’s abilities to control their behavior in low stress and high stress situations are not fully developed until the early 20s, so adolescents may seem like adults, at least in low stress situations, but their brains are not mature. They often have trouble avoiding risks and controlling impulses.
Teachers can take advantage of this by implementing topics such as history, literature, family, school, and positive belief can help them mature their brains and give them the opportunity to take risks.
9. How does the brain work? What is brain plasticity?
The brain processes information that it receives from the senses and body, and sends messages back to the body, but the brain can do more than a machine, for example the brain make humans think, experience emotions with their brain, and it is the root of intelligence. Brain plasticity is the constant change in neurons, synapses, and activity. Thanks to this the brain is changing, shaped by activity culture, and context.
10. How can teaching have an effect on brain development?
It varies because all we know that we have two hemispheres, the left controls the right and the right controls the left. When one of the hemispheres are damaged because of an accident it affects the person learning.
11. What can be learned from neuroscience? What are some of the teaching implications? (p. 49)
Human capabilities intelligence, communication, and problem solving emerge from each person’s unique synaptic activity on their genetically endowed brain anatomy. Many cognitive functions are differentiated; they are associated with different parts of the brain, so learners are likely to have preferred modes of processing visual or verbal as well as varying capabilities in these modes.The brain relatively plastic, so enriched, active environments and flexible instructional strategies are likely to support cognitive development in young children and learning in adults. Some learning disorders may have a neurological basic; neurological testing may assist in diagnosing and treating these disorders.
12. According to Piaget what four factors influence cognitive development?
Biological maturation, activity, social experiences, and equilibration.
13. What are the two basic tendencies we humans inherit according to Piaget?
14. What is the process of Equilibrium? Explain.
In Piaget’s theory, the actual changes in thinking take place through the process of equilibration the act of searching for a balance. The equilibration process works if we apply a particular scheme to an event or situation and the scheme works, then equilibrium exists, but if the scheme does not produce a satisfying result, then it is disequilibrium exists and we become uncomfortable.
15. What are the four stages of cognitive development? Briefly describe each.
INFANCY: SENSORIMOTOR STAGE: During this period, infants develop object permanence, the understanding that objects exist in the environment whether they perceive them or not. This is the beginning of the important ability to construct a mental representation.
EARLY CHILDHOOD TO THE EARLY ELEMENTARY YEARS: THE PREOPERATIONAL STAGE: The child is moving toward mystery but has not yet mastered these mental operations. The ability to form and use symbols, words, gestures, signs, images, an so on is thus a major accomplishment of the preoperational period and moves children closer to mastering the mental operations of the next stage.
LARGE LEMENTARY TO THE MIDDLE SCHOOL YEARS: THE CONCRETE-OPERATIONAL STAGE: Recognition of the logical stability of the physical world, the realization that elements can be changed or transformed and still conserve many of their original characteristics, and the understanding that these changes can be reversed.
HIGH SCHOOL AND COLLEGE: FORMAL OPERATIONS: The focus is thinking can shift from what is to what might be. The formal operational thinker can consider a hypothetical situation and reason.
16. Explain adolescent egocentrism.
Adolescents do not deny that other people may have different perceptions and beliefs, they become very focused on their own ideas. They spent much time examining their own beliefs and attitudes. The adolescents believed that others are analyzing them. This explains why many students at this age develop interests in utopias, political causes, and social issues. They want to design better worlds, and their thinking allows them to do so. Adolescents also can imagine many possible features for themselves and may try to decide which is best. Feelings about any of these ideals may be strong.
17. According to Vygotsky, how is cognition developed?
Vygotsky believed that human activities take place in cultural settings and that they cannot be understood apart from these settings. One of his key ideas was that our specific mental structures sand processes can be traced to our interactions with others. These social interactions are more than simple influences on cognitive development they create our cognitive structures and thinking processes. In fact, Vygotsky conceptualized development as the transformation of socially shared activities into internalized processes.
18. What is the role of private speech?
Private speech play an important role in cognitive development because they move children in stages toward self-regulation the ability to plan, monitor, and guide your own thinking and problem solving. Child’s behavior is regulated by others using language and other signs such as gestures.
19. What is the Zone of Proximal Development? What implications does this concept have for us teachers?
Is the area between the child’s current performance and the level of performance that the child could achieve with adult guidance or by working with a more fully developed child. It is a dynamic and changing space as student and teacher interact and understanding are exchanged. It could be an implication for us because if the student is not mature enough or if he/she is shy and they cannot perform because their parents do not help them at home, we must help them by making instruction focused in each student’s ZPD developing new skills. Students are most receptive to instruction within their ZPD because it represents the next logical step in their ongoing skill development in contrast, without reliable information on student’s constantly evolving ZPDs, it is difficult to identify who is ready for more challenging material and who needs additional assistance.
 Moral development
Moral development
1. What are the different Parenting Styles?
Authoritative parents: Set clear limits, enforce rules, and expect mature behavior, but they are warm with their children. They listen to concerns, give reasons for rules, and allow more democratic decision making.
Authoritarian parents: Seem cold and controlling in their interactions with their children. Kids are expected to be mature and to do what the parents says, there is no much talk about emotions.
Permissive parents: Warm and nurturing, but they have few rules or consequences for their children and expect little in the way of mature behavior.
Rejecting/ Neglecting/ Uninvolved parents: Don’t seem to care at all and can’t be bothered with controlling, communicating, or teaching their children.
2. How are the Latino Families described?
They are characterized as protective, or authoritative, they tend to be more demanding and less likely to grant autonomy to their female children.
3. What is attachment? What implications does it have for teachers?
Attachment is the emotional bond that forms between people. It has implications when the student form insecure or disorganized attachments with other people because maybe the parents are guilty to control and protect their child, so when they are in the school their confidence would be a problem, is there is something wrong they will not trust us until they feel comfortable with us.
4. What are some of the recommendations to deal with children of divorce?
Take note of any sudden changes in behavior that might indicate problems at home
Talk individually to students about their attitude or behavior changes.
Help students maintain self-esteem.
Be sensitive to both parents’ rights to information
5. How powerful is peer pressure? Explain
From an adolescent perspective, it is very important for them to belong on a peer group because of it depends their lives. Why? Because they do not believe in themselves, they need someone else opinion to make decisions, and they trust more on friends rather than their parents. Also, it made them feel important and special, even though they are not in the popular crowd.
6. What could be some causes of Rejection?
Being different
Thinking different
Having opposing views
Different beliefs
7. Briefly describe Erikson's theory.
Emphasizes emergence of the self, the search for identity, the individual’s relationships with others, and the role of culture throughout life.
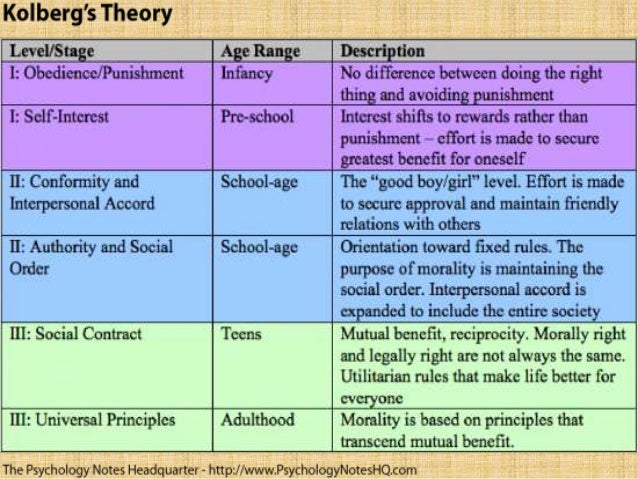
8. What are the stages of Moral Development? Explain each.
Preconventional Level:
Stage 1. Obedient orientation: obey rules to avoid punishments and bad consequences.
Stage 2: Reward/ Exchange Orientation: Right and wrong is determined by personal needs and wants.
Conventional Level:
Stage 3: Being nice/ Relationships Orientation: Being good means being nice and pleasing others.
Stage 4: Law and Order Orientation: Laws and authorities must be obeyed; the social system must be maintained.
Postconventional level:
Stage 5: Social Contact Orientation: The moral choice is determined by socially agreed upon standards.
Stage 6: Universal Ethical Principles Orientation: There are universal principles of human dignity and social justice that individuals should uphold, regardless of the law and no matter what other people say.
Learner differences and Laerning needs
1. What is intelligence?
Intelligence is the ability to acquire and apply knowledge and skills.
2. How can intelligence be measured?
The intelligence can be measure by making a standardize test which tell us how old our intelligence quotient is, and it measures our cognitive abilities in relation with our age.
3. How can Gardner's multiple intelligences be implemented in the classroom?
For each category of multiple intelligence, we can include an activity that addresses to the students in the area that they have to improve, for example
- Musical Intelligence: A lesson
that involves music, it could be to make the students complete a lyric of the
song while they listen to it and fill in the blanks with the words that are
missing we can use this activity for a grammar topic.
- Linguistic Intelligence: An activity
could be a debate in class by making two different groups one for agree and the
ones that disagree on a topic of their interest.
- Mathematical
Intelligence: To make a mathematic interesting class the teacher can
ask them to complete a Sudoku it helps them think, analyze, and keep them busy
for long time.
- Kinesthetic Intelligence: For first
graders we can teach them the parts of the body with a song so they will
remember it for the rest of their lives.
- Spatial Intelligence: Asking
students to draw a chart or a conceptual map which they feel more comfortable
to learn about a topic.
- Intrapersonal Intelligence: Activities
such as collaborative online forums and chat programs enable intrapersonal
intelligence learners to help others and to share experiences and ideas.
- Interpersonal Intelligence: Activities
could be movies, team gams, conversations or conferences.
- Naturalist Intelligence: Making activities outdoors for the first day of school, so in this way they can ask the student to find something that represents them.
4. What
factors can affect an individual's I.Q? Explain
It can affect on sex differences, race and ethnicity, it also has to do with problem solving, skills because according to Lindberg (2010) males are more common to know mathematics than girls, in physics boys are likely to be interested why? Because as I understood their skills are more developed. I think that both male and female can deal with physics, we both can play videogames women can not be as good as men, but we both can solve math problems, study physics.
5. What are learning and thinking styles and what strategies can teachers use to help learners?
Learning style is how a person receive information, it could be auditory, visual, or tactile. Thinking style is how a person process information. A strategy that the teacher should use to help them is to adapt the class to each learner for example, for each topic the instructor should find a way to teach every topic using their senses, so with this approach learners would be more interested in the subject. If the students go to another school or with another teacher that does not use this method, when they are studying, they can apply this technique according to their learning style.
6. What are the greatest challenges teachers face when dealing with students with special needs?
- Amount
of paperwork such as forms, evaluations, and reports among other things.
- Communication
between student’s parents, and teacher’s therapists to keep everyone on the
same page and answer questions if something is unclear or a problem arises.
- Collaborating
with general education teachers to gain a better understanding of the learner.
- Data
collection to back up evidence of every claim that students make.
7. What strategies should teachers implement to best deal with this population?
Sometimes at first sight we can identify if a person does have a special need or not, but there are cases in which we should pay close attention to our students and realize that they deserve a special treatment. Here is when we should be aware to any situation such as adapting the class in an inclusive way, every day trying to make the learners comfortable in the classroom and to teach them that we all are similar but different at the same time without making any discrimination, and also taking into consideration everyone opinion and motivate them by telling that their ideas are valid.
8. How can teachers best serve gifted learners? Explain.
- Pretest
for Volunteers
- Speak
to students interests
- Enable
gifted students to work together
- Plan
for tiered learning
Using these strategies will help the gifts students to get involve in the class and make them participate, it also, advise them to develop more skills and guide the classmates that have weaknesses on the subject. This can generate conflict with the smart learners because they may feel underestimated if the teacher does not apply an equal strategy for everyone.
Language development, diversity, and immigrant education
1. Explain the concept of OVERREGULARIZING. Think of typical examples in Spanish.
Overregularizing are regular grammatical patterns to irregular words, resulting in overregularizations come after a period of correct performance. The errors seem paradigmatic of rule use, hence bear on central issues in the psychology of rules. Examples in Spanish are pieses, haiga, vistes, hiba, nadien, ollí y dijistes.
2. What are pragmatics? Illustrate with examples.
A: I have a 14 year old son
B: Well that’s right
A: I also have a dog
B: Oh, I’m sorry
3. Should teachers focus more on decoding or oral skills? Explain.
I think that both are equal important to teach and for a children to
learn no matter which their learning style is. As the book says these skills
often support each other, however it indicates that early in the learning to
read process in English, decoding skills are more important because students
need to become fast and automatic in processing letters and words so they have
more mental resources available for comprehending what they read.
4. How can family and school support language and promote literacy? Provide some ideas.
The family can red with the kid to help the children understand that
books contains stories, that they can visit the stories as often as they like,
that the pictures in the books go along with the story meaning, and that the
words are always the same when they visit the story. Also they can choose
appropriate books and stories with simple plots and clear illustrations, make
sure those pictures precede the text related to the illustration. This helps
the child to learn to predict what is coming next. Ensure that language is
repetitive, rhythmic, and natural.
The teacher should use stories as a springboard for conversations to
retell stories you have read with your students, talk about the words,
activities, and objects in the books. Do the student have anything like these
in their home or classroom.
5. what is the difference between early bilingualism (before age 5) and later bilingualism.
Bilingual children may have a larger vocabulary in the language that
they are learning from the person with whom they spend the most time or have
the closest bond. The earlier people learn a second language, the more their
pronunciation is near native, this is because from birth to about 4 months,
infants can discriminate all the basic sound building blocks from any of the
world’s 6,000 or so languages. On the other hand, later bilingualism it is
almost impossible to learn a new language without speaking with an accent, even
if a child overhears a language, without actually learning it formally, this
can improve later learning.
6. Is there a critical period for language? Explain.
There is no critical period that limits the possibility of language
learning by adults. In fact older children go through the stages of language
learning faster than young children. Adults have more learning strategies and
greater knowledge of language in general to bring to bear in mastering a second
language.
7. What are some clear benefits of bilingual?
- Learning English as a second language takes 2-3 years
for ora and 5-7 years for academic language use.
- Reading is the skill that transfers most readily.
- Code-switching indicates high-level language skills in
both L1 and L2.
8. How different can ELLs be?
Very different because they are people that just learned the language
from their country, unlike bilinguals or monolinguals it is very difficult for
them to learn a new language because of its remarkable accent, and for them
there are some words they could never pronounce.
9. What are the two basic approaches to teaching
ELLs? Which one would you support?
The two basic
approaches are research on bilingual education and bilingualism for all the two
way immersion, and I support the second one that I mentioned because in this
one the teacher is able to teach ELLs with some techniques such as using
vocabulary in the language the instructor is teaching without taking to switch
to the other language by using examples, drawings, vocabulary, synonyms and so
on to explain or repeating an instruction if the student does not understand,
so in this way the learners are forced to learn a second language being fair
with the other classmates even though this student has any disability.
Behaviorism
 Please watch video and read
chapter. Then write a reaction paper stating the most salient points introduced
in both the chapter and the video.
Please watch video and read
chapter. Then write a reaction paper stating the most salient points introduced
in both the chapter and the video.
Watson focused his theory on a nine-month-old boy that had phobia of
small fluffy creatures, which is very unethical by today’s standards, but well
to shape our ideas about how learning affects behavior. According to this
experiment Watson want to provide that babies can grow up being a doctor,
dentist, thief’s, and so on, depending on the environment in which they rise.
The behavior of the child with this experiment they develop fears, faith,
happiness, confidence, love, etc.
I think that both are equal important to teach and for a children to learn no matter which their learning style is. As the book says these skills often support each other, however it indicates that early in the learning to read process in English, decoding skills are more important because students need to become fast and automatic in processing letters and words so they have more mental resources available for comprehending what they read.
4. How can family and school support language and promote literacy? Provide some ideas.
The family can red with the kid to help the children understand that books contains stories, that they can visit the stories as often as they like, that the pictures in the books go along with the story meaning, and that the words are always the same when they visit the story. Also they can choose appropriate books and stories with simple plots and clear illustrations, make sure those pictures precede the text related to the illustration. This helps the child to learn to predict what is coming next. Ensure that language is repetitive, rhythmic, and natural.
The teacher should use stories as a springboard for conversations to retell stories you have read with your students, talk about the words, activities, and objects in the books. Do the student have anything like these in their home or classroom.
5. what is the difference between early bilingualism (before age 5) and later bilingualism.
Bilingual children may have a larger vocabulary in the language that they are learning from the person with whom they spend the most time or have the closest bond. The earlier people learn a second language, the more their pronunciation is near native, this is because from birth to about 4 months, infants can discriminate all the basic sound building blocks from any of the world’s 6,000 or so languages. On the other hand, later bilingualism it is almost impossible to learn a new language without speaking with an accent, even if a child overhears a language, without actually learning it formally, this can improve later learning.
6. Is there a critical period for language? Explain.
There is no critical period that limits the possibility of language learning by adults. In fact older children go through the stages of language learning faster than young children. Adults have more learning strategies and greater knowledge of language in general to bring to bear in mastering a second language.
7. What are some clear benefits of bilingual?
- Learning English as a second language takes 2-3 years
for ora and 5-7 years for academic language use.
- Reading is the skill that transfers most readily.
- Code-switching indicates high-level language skills in
both L1 and L2.
8. How different can ELLs be?
Very different because they are people that just learned the language from their country, unlike bilinguals or monolinguals it is very difficult for them to learn a new language because of its remarkable accent, and for them there are some words they could never pronounce.
9. What are the two basic approaches to teaching
ELLs? Which one would you support?
The two basic approaches are research on bilingual education and bilingualism for all the two way immersion, and I support the second one that I mentioned because in this one the teacher is able to teach ELLs with some techniques such as using vocabulary in the language the instructor is teaching without taking to switch to the other language by using examples, drawings, vocabulary, synonyms and so on to explain or repeating an instruction if the student does not understand, so in this way the learners are forced to learn a second language being fair with the other classmates even though this student has any disability.
Behaviorism
Pavlov a Russian scientists whose interest on the digestive systems of dogs noticed an unusual effect, the dog loved salivate before they saw the food they were salivating as they heard the researchers walking towards him down the corridor that made Pavlov wonder what the process was, I wish dogs associate the sound of the fee with the food. On the contrary to Watson, he had to adapt the dog to salivate every time he rings a bell, Watson use toys, to demonstrate how the baby feel with those elements. BF Skinner is famous for his Skinner box where he placed rats and pigeons inside a contraption which would give food, it released after the pigeon or the rat pressed a lever. There were some variations, the Skinner box sometimes had lights, or the floor would be electrocuted. The principle key for these areas was that psychology should be fundamentally scientific that could be measured objectively with a stimulus. Skinner and Pavlov had the same methodology, but they use it with different animals, they repeat a sound, or turn on and off the lights to make sure the creatures understand what they must do.
It is very interesting that humans had a different learning approach than animals, I mean it because with one mistake you do with a baby he will cry, you don not need to do it again to listen it sobbing, only if you are so mean and you like the sound they make. With animals you must repeat the movements to make him understand what you want.
MEMORY
1. What are other names given to sensory memory?
Sensory buffer, iconic memory, and echoic.
2. What is the difference between working memory and short memory?
Work memory is where the information is temporary held and combined with knowledge from the long-term memory to solve problems or comprehend a lecture, in the contrary, short-term memory storage the immediate memory for new information that can be held about 15 to 20 seconds.
3. What are strategies teachers can use to get students' attention?
- Using signals
- Reach out
rather than call out
- Make sure the
purpose of the lesson or assignments are clear to student
- Incorporate variety, curiosity, and surprise
- ask
questions and provide frames for answering
4. What is selective attention and why is this important?
Selective attention is focusing on an object for a period while ignoring irrelevant information that is happening at the same time. This is important because there are people who had deficit disorder whose consideration may be a distraction and individuals that focus on what is important, we as teachers must pay attention to learners with this disability.
What are the two types of Multitasking?
- Sequential multitasking when you switch back and forth
from one task to another, but focusing on one at a time
- Simultaneous multitasking when there is overlapping
focus on several tasks at a time.
6. Why do we forget information?
Because we are not paying attention to what is said, we are distracted with other things, the information given is not important for us, the person who gives the instruction is not clear, or do not ask for our attention to listen to them, noises from outside can interfere when someone is talking so, this can interrupt the information that we receive.
7. What are the different kinds of KNOWLEDGE? Provide an original example for each.
Domain specific knowledge: Playing chess to make them think creatively and strategically
8. As a teacher how can you help your students to retain information?
I could have a bowl with the name of each student, so at the beginning of the class I will tell them that they have to pay attention to my class because they have to participate, if they do not raise their hand I will pick up a name from the pot and that person will talk. Another technique is to talk and ask someone to repeat what I said and continue, every time I tell them an instruction, I will choose a name from the bowl and that student will repeat.
Analyzing the student (classmate analysis)
The Goldfish
As the final school bell rings, most of the
students in Ms. Bowman’s first-grade
class gather their belongings and hurry out the
door. But Amy convinces her friend
Lucy to linger for a few minutes while
she checks on Ringo, the class’s pet goldfish.
As this week’s “animal keeper” for the class,
Amy has noticed that Ringo hasn’t eaten
any of his food for the past two days. In fact,
all he does now is lie sideways on the
surface of the water; he doesn’t try to swim
away anymore when she touches him.
With her friend looking over her shoulder, Amy
tries to give the fish a slight push
towards a few flakes of food.
“He must be sleeping,” she says. “Usually all I
have to do is swish the water
around to make him swim. He’s acting really
weird. Maybe he’s forgotten how to eat
and swim.”
Lucy inspects the fish and then looks back at
her friend, “I don’t know, Amy.
He’s been sleeping an awful long time. He’s not
eating, either. I’ll get Ms. Bowman,
and maybe she can fix him.”
Lucy hurries over to her teacher and grabs her
by the hand. “Something’s
wrong,” Amy declares as Lucy and Ms. Bowman
approach the fish bowl. “He’s not
moving. He hasn’t eaten for a long time.”
When Ms. Bowman looks in the bowl, she realizes
that Ringo has died. She
delicately explains the situation and then wraps
the fish in a paper towel. She assures
the girls that she will give Ringo a proper
burial as soon as she gets home.
Amy looks puzzled. “But...but...when my grandpa
died last summer, he went
away to heaven and didn’t come back. Ringo’s
still here. If he’s dead, he should be
going to heaven.”
“Do you want Ringo to go to heaven. ” Amy nods,
and her teacher smiles.
“Well, then, I’ll bet he’ll go there just as
soon as he possibly can.”
As the two girls walk home, Lucy poses a
question. “Do you have to eat in
heaven?”
“I don’t know,” Amy responds. “I suppose so, or
else you’d be hungry all the
time.”
“Oh, that makes sense.” Lucy pauses for a
moment, then asks, “Well, do you
have to go potty in heaven?”
Amy rolls her eyes, indignantly puts her hands
on her hips, and replies, “Of
course not, silly! You know our Mommies and Ms.
Bowman make us go potty
before we go anywhere!”
“Oh, yeah, I forgot,” laughs Lucy.
Analyzing the teacher
Peter is a middle school science teacher who motivate his students with
positive messages. He begins each class with an ice break activity about the
previous topic he taught, which help them participate and work in their memory.
Because it consists on making a circle and they must pass each other a drum and
said what they did last class. Everyone has to say something about it unless
they were not in the lesson. He teaches this way considering that when he was younger,
he felt isolated, so his experience advises him to involve his students by
making them feel important, and part of the class.
Even though he is a science teacher, he taught them his own cultural
identity because he thinks they do not have culture. This takes place in many
ways, from pictures of Native American chiefs displayed around the room, to his
use of the talking circle in which each student shares their memory of science
the previous day. He also encourages the visitors to his classroom to share
their identity with his learners. He taught them science with real life
situations, so they can relate what they learn with any context. Also, he gave
them the opportunity to give their point of view for example, they were talking
about the European explorers that went to Australia, so he asked them ‘imagine
how the European explorers must have felt when they saw the continent of
Australia for the first time? What about the individuals who had been there for
long as that continent has been there?’ This way they can discuss the questions
and create a debate about the topic, and make the students have their opinion
about it. Pete learn from the kids, interact with them, get to know each other
at once rather than analyzing, studying, judging them since the beginning of
the year, something that teachers should do to create confidence, support,
help, and love, even for those kids that are in risk.
This case told me something that can help teachers to take a lesson
easier, comprehensive and that can make the students learned it and never
forget about it. There is a reason why every teacher teaches the way they do it
and it is called experience. The background that we had when we were students,
help us to decide how we want to teach because if we had a bad memory of a
lesson then we can think about how it was and consider another way to explain
the same topic that make the students understand and take it to their good
thoughts. This is important because according to Henry Levin (1971) says that
teacher experience was related to student performance on standardize
achievement tests. No rigorous study to my knowledge has found that the
teacher’s degree level or the number of college units accumulated is related to
that outcome. This method motivates the student to feel important, part of the
class, seen a person not as a number, in the other hand help teachers to get to
know their learners in terms of their needs, strengths, weaknesses, engage them
to participate if the student never share comments to the class. Even if
learners feel uncapable to answer teachers try their best to help them. Our
goal is to listen everyone and help them with their difficulties.
If I were Pete I will do the same with them because teaching according
to my experience, or taking into consideration the methods from my teachers I
could transmit the same message that I had, it does not mean they will take it
the same way as I did but different and I would be satisfactory of my work.
This could help me also, when I will have kids, I can choose between my
experience with my parents or using their same way to raise my kids. Sometimes
I think that I do not want them to go through the same things that I did. So,
it is better to avoid those situations and let them experience by themselves
because if they do not it, then they will never understand why I do not want
them to do certain things.
Summary
The video begins with a girl who suffer educational stress because of
the tests, the school and its environment. According to the specialists who
speak in the video, they said that this happens as a result of bullying which
is nowadays very common in the school, the discrimination to learners with a
disability, the way professors teach as if everyone has the same intelligence
and methods to learn, and we are all different. A teacher mentions something
very interesting for me and true, people choose to be teachers because they do
not reach the grade to the profession they want, or they like kids, and they
think it is easy to teach. Parents think teachers must raise their child, but
there are things that kids must know from their family. They also want them to
have more homework, so they do not have time to see their friends and parents.
A student also said that teachers do not advise us how to be successful, or how
to face failures they only told us to be better next time and studied more, but
they do not say how or if we need some help, they just assume that we were
lazy, or do not care about school. They do not teach us how to be a leader, or
work in groups. Another guy said something about practicing sports, if I play
sports, he said- I will spend my energy in something that I like and get more
focused on school, more discipline but my parents are afraid of getting
distracted.
Analysis
Teaching is not easy, we should not choose a career just because the one
that we wanted did not accept us. If this happens, they could find advise from
an employment consultant that can help them, so in this way we do not have bad
teachers in the future. If we want to be teachers, we must love it, enjoy it,
not because we like kids we are going to become professors, we can be baby
sisters as well. Instructors should be aware of their students’ necessities, if
they had a learning disorders, we must help them, study them, and find a way to
make them improve engaging the class. We can focus on our learners without
having a favorite, we can adapt the class in the way that everyone understands
and enjoys it, and advice the teachers from the next year to do the same, so in
this way they do not regret about passing the year. The professor will may not
be using the same methodology, but they could improve something more interesting
according to their age. Nowadays the word bullying is everywhere I listen to
teachers saying stop it, but they do not something thereon, they may teach them
positive ways to treat this problem. I think that if we pay attention to our
kids as parents or teachers everything for them would be better. If they ask us
for something that we think is a distraction for them, let them have it maybe
not, you will see why in a moment.
Experience
In my school years I have been a good girl, but I used to have attention
deficit disorder, so my mother took me to psychologists, and specialists to
improve my attention, but it does not work because I used to take Ritalin. It
was my mom solution for me because since I take it my grades went better, until
doctors declare it a drug, at that moment she investigates and bought me
homeopathy for high school. I used to sit on the front, and I do not like it
because I felt a pressure of the teacher watching me, that I cannot talk to
anyone because the professor will call my attention. When I had the opportunity
to sit on the back I took advantage of it, I got distracted of course, but I
enjoy it when I could. I remembered that I wanted a play station or a Wii, but
my parents does not want me to get distracted on the school, funny fact because
three years ago I bought me one and believed or not it helps me to get
inspired. When I have things to do for college and I am stress about it I think
I am going to play and then I will do projects, while I am playing Mario kart
many ideas come through my head it is impressive. I have a game on my cellphone
called clash of clans and every time I’m not focus, I play and then I continue
with my tasks like nothing would happen. If they had bought me a play station
when I ask them to have it may be, I would not be that distractive and they not
had to waste a lot of money in Ritalin or in psychologists.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/1449117-article-gifted-children-and-language-development-01-5aa81c37ba61770037a70b26.png)

Comentarios
Publicar un comentario